En respuesta al anuncio del alcalde Ismael Burgueño Ruiz sobre...
Leer más
Factors Influencing COVID-19-Related Mortality Risk in T2DM Patients
Takeaway
- Several factors are likely to influence the risk of subsequent COVID-19-related mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) following a confirmed COVID-19 infection.
- The use of metformin, sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2is), and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) agonists and a non-smoking status were associated with a lower risk of COVID-19-related mortality in patients with T2DM.
- Age, T2DM, male sex, and social disadvantage were linked to an increased risk of COVID-19-related mortality.
Why This Matters
- The findings have led to a better understanding of the factors that put patients with T2DM at a higher risk of becoming seriously ill and dying following COVID-19 infection.
Study Design
- A retrospective case-control study used data from the Greater Manchester Care Record (GMCR) database (2020-2021).
- 13,807 patients with T2DM and subsequent confirmed COVID-19 infection (T2DM group) were matched (1:3) with 39,583 participants without T2DM and with confirmed COVID-19 infection (control group).
- Funding: None.
Key Results
-
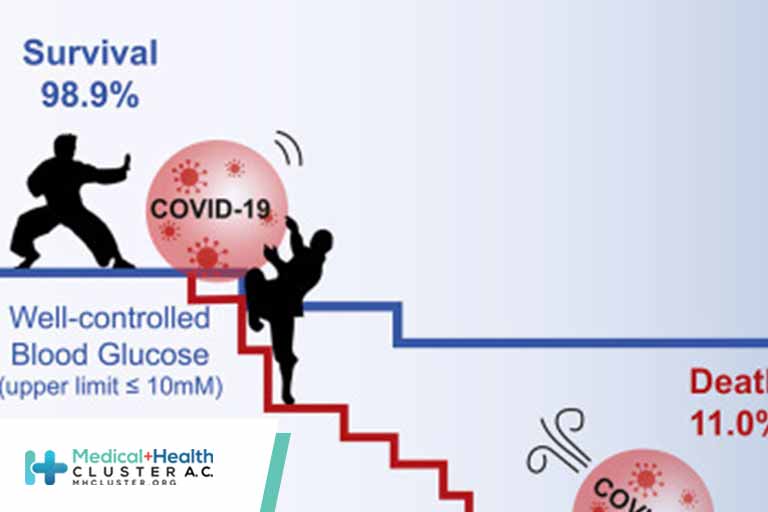
- The COVID-19-related mortality rate was significantly higher in the T2DM vs control group (7.7% vs 6.0%; P<0.001).
- In the T2DM group, the risk of COVID-19-related mortality was lower among (OR; 95% CI):
- metformin users (0.494; 0.435 to 0.560);
- SGLT2i users (0.299; 0.226 to 0.388);
- GLP-1 agonist users (0.680; 0.464 to 0.960); and
- non-smokers.
- In the combined analysis of the T2DM and control groups, factors independently associated with a higher risk of COVID-19-related mortality were (adjusted OR; 95% CI):
- T2DM (1.318; 1.159 to 1.498);
- age (1.105; 1.099 to 1.112);
- male sex (1.432; 1.267 to 1.621); and
- social deprivation (higher Townsend score; 1.050; 1.032 to 1.068).
Limitations
- Retrospective design.
Créditos: Comité científico Covid