En atención a la creciente preocupación sobre la confianza en...
Leer más
When You’ve Been Fully Vaccinated
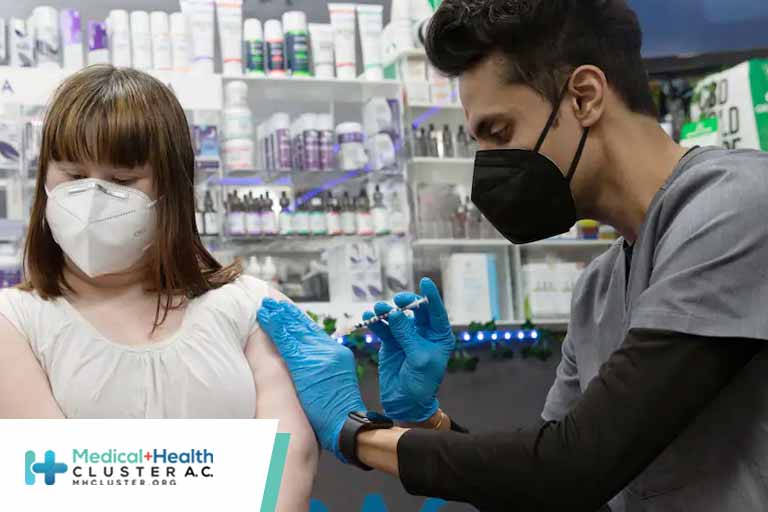

COVID-19 vaccines are effective at protecting you from getting sick. Based on what we know about COVID-19 vaccines, people who have been fully vaccinated can start to do some things that they had stopped doing because of the pandemic.
We’re still learning how vaccines will affect the spread of COVID-19. After you’ve been fully vaccinated against COVID-19, you should keep taking precautions—like wearing a mask, staying 6 feet apart from others, and avoiding crowds and poorly ventilated spaces—in indoor public places until we know more.
These recommendations can help you make decisions about daily activities after you are fully vaccinated. They are not intended for healthcare settings.
Have You Been Fully Vaccinated?
In general, people are considered fully vaccinated: ±
- 2 weeks after their second dose in a 2-dose series, such as the Pfizer or Moderna vaccines, or
- 2 weeks after a single-dose vaccine, such as Johnson & Johnson’s Janssen vaccine
If you don’t meet these requirements, you are NOT fully vaccinated. Keep taking all precautions until you are fully vaccinated.
If you have a condition or are taking medications that weaken your immune system, you may NOT be fully protected even if you are fully vaccinated. Talk to your healthcare provider. Even after vaccination, you may need to continue taking all precautions.
What You Can Start to Do
If you’ve been fully vaccinated:
- You can gather indoors with fully vaccinated people without wearing a mask or staying 6 feet apart.
- You can gather indoors with unvaccinated people of any age from one other household (for example, visiting with relatives who all live together) without masks or staying 6 feet apart, unless any of those people or anyone they live with has an increased risk for severe illness from COVID-19.
- You can gather or conduct activities outdoors without wearing a mask except in certain crowded settings and venues.
- If you travel in the United States, you do not need to get tested before or after travel or self-quarantine after travel.
- You need to pay close attention to the situation at your international destination before traveling outside the United States.
- You do NOT need to get tested before leaving the United States unless your destination requires it.
- You still need to show a negative test result or documentation of recovery from COVID-19 before boarding an international flight to the United States.
- You should still get tested 3-5 days after international travel.
- You do NOT need to self-quarantine after arriving in the United States.
- If you’ve been around someone who has COVID-19, you do not need to stay away from others or get tested unless you have symptoms.
- However, if you live in a group setting (like a correctional or detention facility or group home) and are around someone who has COVID-19, you should still stay away from others for 14 days and get tested, even if you don’t have symptoms.
What You Should Keep Doing
For now, if you’ve been fully vaccinated:
- You should still protect yourself and others in many situations by wearing a mask that fits snugly against the sides of your face and doesn’t have gaps. Take this precaution whenever you are:
- In indoor public settings
- Gathering indoors with unvaccinated people (including children) from more than one other household
- Visiting indoors with an unvaccinated person who is at increased risk of severe illness or death from COVID-19 or who lives with a person at increased risk
- You should still avoid indoor large gatherings.
- If you travel, you should still take steps to protect yourself and others. You will still be required to wear a mask on planes, buses, trains, and other forms of public transportation traveling into, within, or out of the United States, and in U.S. transportation hubs such as airports and stations. Fully vaccinated international travelers arriving in the United States are still required to get tested within 3 days of their flight (or show documentation of recovery from COVID-19 in the past 3 months) and should still get tested 3-5 days after their trip.
- You should still watch out for symptoms of COVID-19, especially if you’ve been around someone who is sick. If you have symptoms of COVID-19, you should get tested and stay home and away from others.
- You will still need to follow guidance at your workplace.
- People who have a condition or are taking medications that weaken the immune system, should talk to their healthcare provider to discuss their activities. They may need to keep taking all precautions to prevent COVID-19.
What We Know
- COVID-19 vaccines are effective at preventing COVID-19 disease, especially severe illness and death.
- Other prevention steps help stop the spread of COVID-19, and that these steps are still important, even as vaccines are being distributed.
What We’re Still Learning
- How effective the vaccines are against variants of the virus that causes COVID-19. Early data show the vaccines may work against some variants but could be less effective against others.
- How well the vaccines protect people with weakened immune systems, including people who take immunosuppressive medications.
- How well COVID-19 vaccines keep people from spreading the disease.
- Early data show that the vaccines may help keep people from spreading COVID-19, but we are learning more as more people get vaccinated.
- How long COVID-19 vaccines can protect people.
As we know more, CDC will continue to update our recommendations for both vaccinated and unvaccinated people. Until we know more about those questions, everyone—even people who’ve had their vaccines—should continue taking steps to protect themselves and others when recommended.
Want to learn more about these recommendations? Read our expanded Interim Public Health Recommendations for Fully Vaccinated People.
Créditos: Comité científico Covid