Guideline title ACG Clinical Guidelines: Prevention, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Clostridioides difficile Infections Release date May 18, 2021 Prior version 2013 Developer American College of Gastroenterology (ACG) Funding source ACG Target population Adults with suspected or diagnosed Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) Major recommendations Initial CDI should be treated with vancomycin or fidaxomicin (strong recommendation; moderate-quality evidence). Metronidazole may be considered […]
Read More
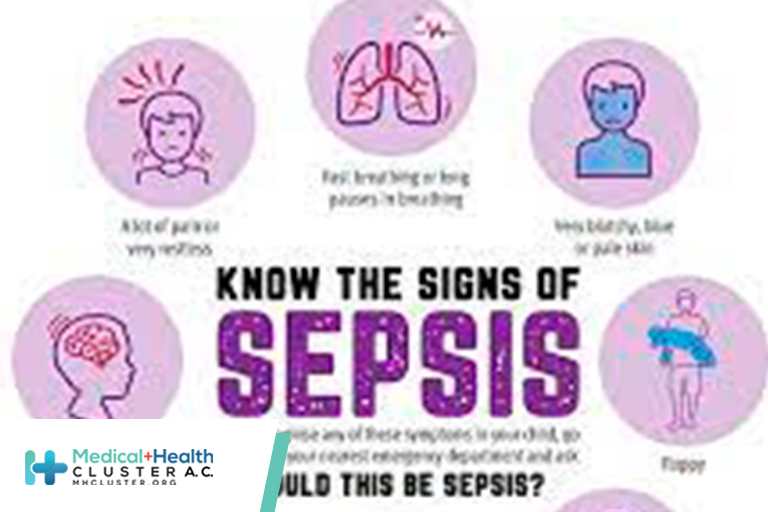
Anyone can get an infection, and almost any infection, including COVID-19, can lead to sepsis. In a typical year: At least 1.7 million adults in America develop sepsis. At least 350,000 adults who develop sepsis die during their hospitalization or are discharged to hospice. 1 in 3 people who dies in a hospital had sepsis […]
Read More
Monkeypox is a zoonotic orthopoxvirus in the same genus as variola (the causative agent of smallpox).1 A recent global outbreak has led to more than more than 39 000 cases reported as of August 18, 2022.2 Monkeypox is typically self-limited with symptoms generally lasting between 2 and 4 weeks in prior outbreaks. Hospitalization […]
Read More
The B.1.1.529 (omicron) variant of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has a shorter incubation period and a higher transmission rate than previous variants.1,2 Recently, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended shortening the strict isolation period for infected persons in non–health care settings from 10 days to 5 […]
Read More
By testing for both SARS-CoV-2 spike and nucleocapsid antibodies, seroprevalence studies can estimate the proportion of a population with antibodies from previous infection (nucleocapsid antibody or infection-induced seroprevalence) and from infection or vaccination (spike antibody or combined infection- and vaccine-induced seroprevalence). US seroprevalence from July 2020 to May 2021 based […]
Read More
In a Spanish cohort study, adding remdesivir reduced mortality and progression to mechanical ventilation in hospitalized patients with high viral loads and low-grade inflammation. Initiating remdesivir within 5 to 7 days of developing COVID-19 symptoms maximizes this agent’s benefits by targeting the viral phase of illness before the onset of […]
Read More
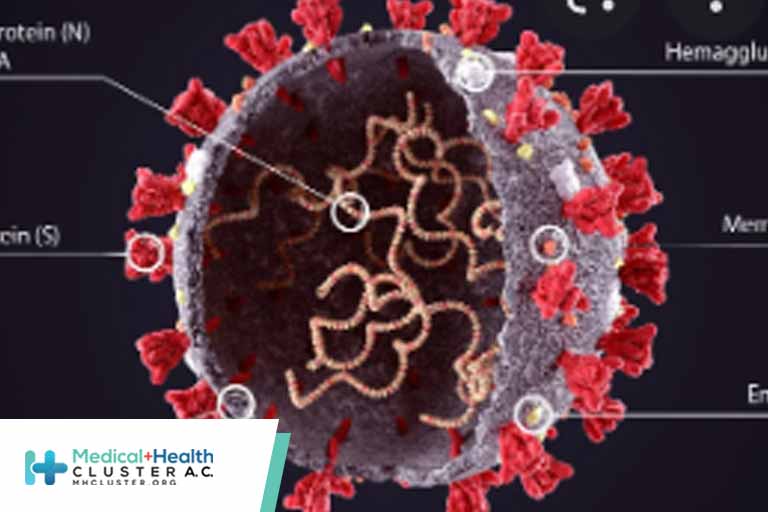
The Catholic University of Louvain (UCLouvain) in Belgium announced that its researchers have managed to identify the key that allows the COVID-19 virus to attack cells. What’s more, they have succeeded in closing the lock to block the virus and prevent it from interacting with the cell, thereby preventing infection. […]
Read More
In a prospective, longitudinal study, N-antibodies peaked 90–100 days after infection and persisted for at least 500 days in most patients. The duration of antibody response after SARS-CoV-2 infection is not clearly established, although prior studies have estimated that antibodies produced after natural infection last from 3 to 6 months. […]
Read More
The incidence of the omicron BA.1/1.1 variant of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which rapidly spread worldwide even among vaccinated persons, is incompletely defined.1 We quantified the incidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection during the initial omicron BA.1/1.1 variant wave among Canadian adults2 and the contribution of previous infection and concurrent vaccination […]
Read More
MADRID, Spain — Clinical experiences in approaching COVID-19 from different perspectives, results obtained by various therapeutic options and, above all, the challenges posed by a new healthcare reality — long COVID — were all the focus of a recent discussion at the 7th International Congress of the Spanish Society of Precision […]
Read More